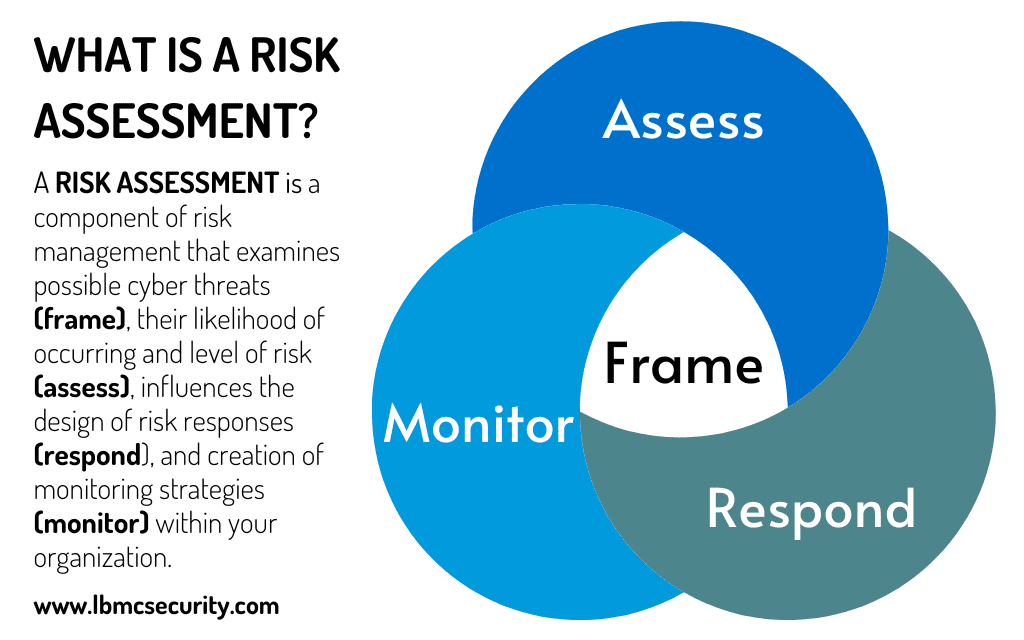
For companies, moving from an informal to a formal risk assessment procedure is absolutely essential. It is not just about following procedures; it significantly improves risk management. For the reasons outlined below, adopting a formal risk assessment process is crucial for security professionals.
Benefits of a Formalized Risk Assessment Process
Security departments that are knowledgeable and informed regarding vulnerability remediation but do not have defined risk assessment processes may find the journey from recognizing gaps to implementing a structured risk assessment process overwhelming at first glance. Organizations often realize they have been spotting risks and identifying vulnerabilities throughout the environment, even in areas lacking defined processes. This emphasizes an important point: security personnel naturally identify risks; however, these risks can go undocumented and unaddressed without formalizing the risk assessment process. Formalized risk assessment procedures help to detect weaknesses and their fixing initiatives even more successfully.
Sharing Risks with Leaders
Risk management in cybersecurity mostly aims to give vital information for executive decision-making rather than to stop corporate projects. With structured risk assessments, insights into security vulnerabilities become extremely valuable for informing key decision-makers and business leaders. This communication ensures that decisions are made with an awareness of risks, a deep understanding of what those risks mean, and a recognition of the inherent dangers associated with those risks.
Six Essential Steps for Establishing an Effective Cybersecurity Risk Assessment Process
A formal risk assessment involves recording everything associated with the risks of a workplace or environment. A great resource for learning how risk assessments are performed is The National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Guide for Conducting Risk Assessments. Fundamentally, the following describes the procedures to establish a formal risk assessment mechanism:
Step 1: Identify Risks
Finding risks includes realizing possible hazards connected to corporate projects, fresh IT innovations, or major organizational adjustments. This covers assigning pertinent threat occurrences and classifying possible sources of risks including antagonistic, accidental, structural, and environmental ones.
Organizations should list possible threat sources and ascertain particular threat occurrences, such phishing campaigns or natural disasters, so properly identifying hazards. This thorough procedure guarantees that every conceivable risk is identified for more investigation.
Step 2: Identify Vulnerabilities
Finding vulnerabilities allows one to grasp how risks could take advantage of organizational flaws. This stage evaluates current security posture and factors that can let the company be vulnerable to failures or attacks.
Organizations should do technical penetration testing and a current state analysis against security models such as NIST CSF. Sort and fully grasp vulnerabilities using NIST 800-30 Appendix F.
Step 3: Evaluate the Risks
Analyzing found risks helps one to comprehend their possible influence and rank them according to probability and importance. This stage helps companies to concentrate on the most important hazards and distribute their resources properly.
Using NIST 800-30 guidelines, one can estimate the probability of each threat event leading to a loss and analyze the possible impact. This dual study offers a thorough image of the risk scene of the company.
Step 4: Calculate Risk
Calculating risk helps to prioritize found hazards by quantifying their possible impact and probability of occurrence. This stage aggregates assessments to create a risk value, hence guiding efforts at strategic risk management.
As stated in NIST 800-30 Appendix I, integrate likelihood and impact values using a 9-block matrix. This methodical technique prioritizes risks from high to low priority, therefore guaranteeing that the most critical are handled first.
Step 5: Mitigate the Risks
Developing and applying plans to control found hazards helps the company to be free from possible risks. This step ensures the organization can maintain operations and security posture.
Develop comprehensive risk mitigation plans addressing high-priority risks, including specific actions like implementing security controls and training staff. Regularly review and update plans to adapt to changing threats.
Step 6: Communicate the Risks
Communicating risks ensures all stakeholders are informed about the organization’s risk landscape and mitigation strategies, fostering a risk-aware culture. Good communication helps attempts at risk management on all levels.
Write thorough risk assessment reports and distribute them, via frequent briefings, to stakeholders and leaders. Effective risk management techniques depend on clear, succinct communication guaranteeing understanding and agreement.
The objective is not to get every recommendation approved but rather to guarantee that every decision is based on a thorough awareness of the hazards and weaknesses entailed.